Using role scope
Overview
This topic explains how to work with role scope and role attributes. A role scope is a resource type by which a role may be parameterized. When you define a role, you can optionally specify a role scope and the parameter, which is called a role attribute.
If multiple members or teams should have similar permissions, but work with different resources, then defining role scope using an attribute key lets you reuse the same role for many members or teams. This means the total number of roles in your account is much smaller, and much easier to maintain.
This topic includes:
- Background information on resources, role scope, and role attributes
- How to define role scope using a role attribute
- How to set a role attribute value when you assign a role to a member or team
- Example: Consolidate existing roles using role attributes
Background: Resources, role scope, and role attributes
When you create a new role, you can specify resources that the role can or cannot access in the following ways:
Role attributes are defined and assigned within LaunchDarkly. They cannot be passed through SAML assertions for single sign-on. For SAML-based SSO, LaunchDarkly supports mapping only the role, customRole, and teamKey attributes.
Define role scope using attribute key
To define role scope using a role attribute when you create a new role policy:
- From the “New role” page, click Advanced to open the “Scope using attribute key” section:
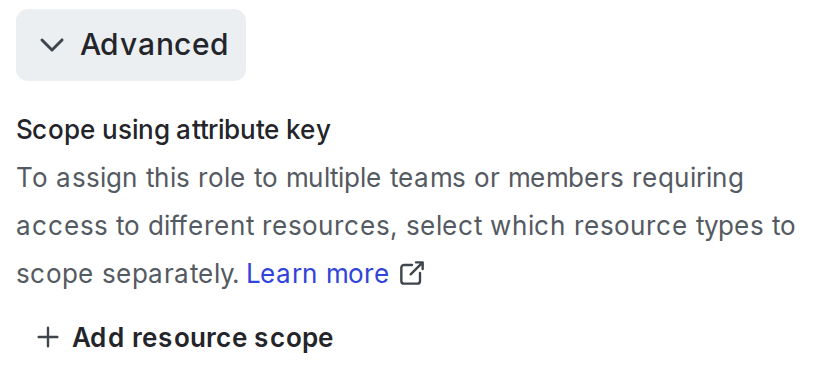
- Click + Add resource type.
- Select a resource type from the menu, for example, “Project.”
- At the prompt, enter a key for the role attribute:
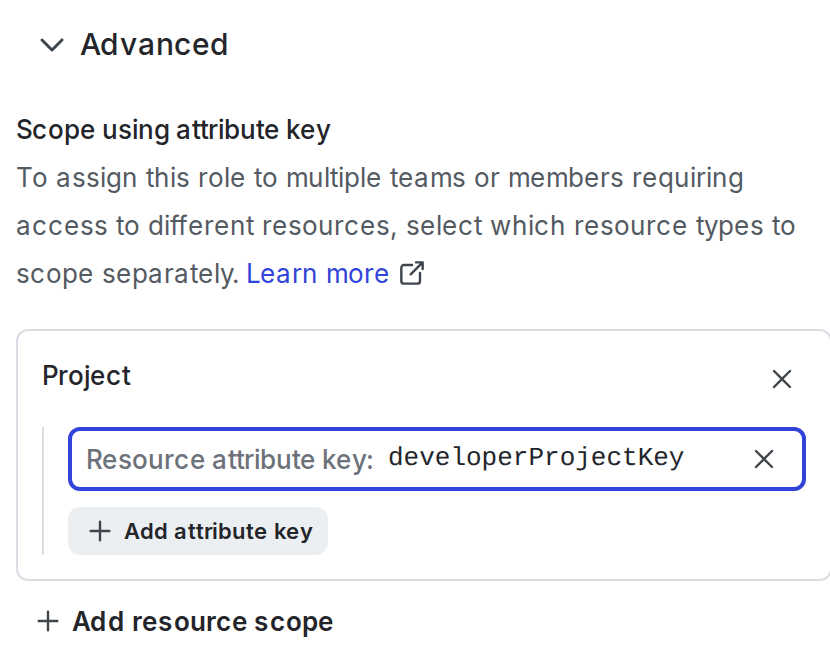
- The role attribute is now a parameter for this role.
- In the role’s policy statements, use the role attribute key any place that you would normally use a specific instance of that resource. For example, if you selected the “Project” resource type in step 3, then you can use the role attribute to allow access only to projects:
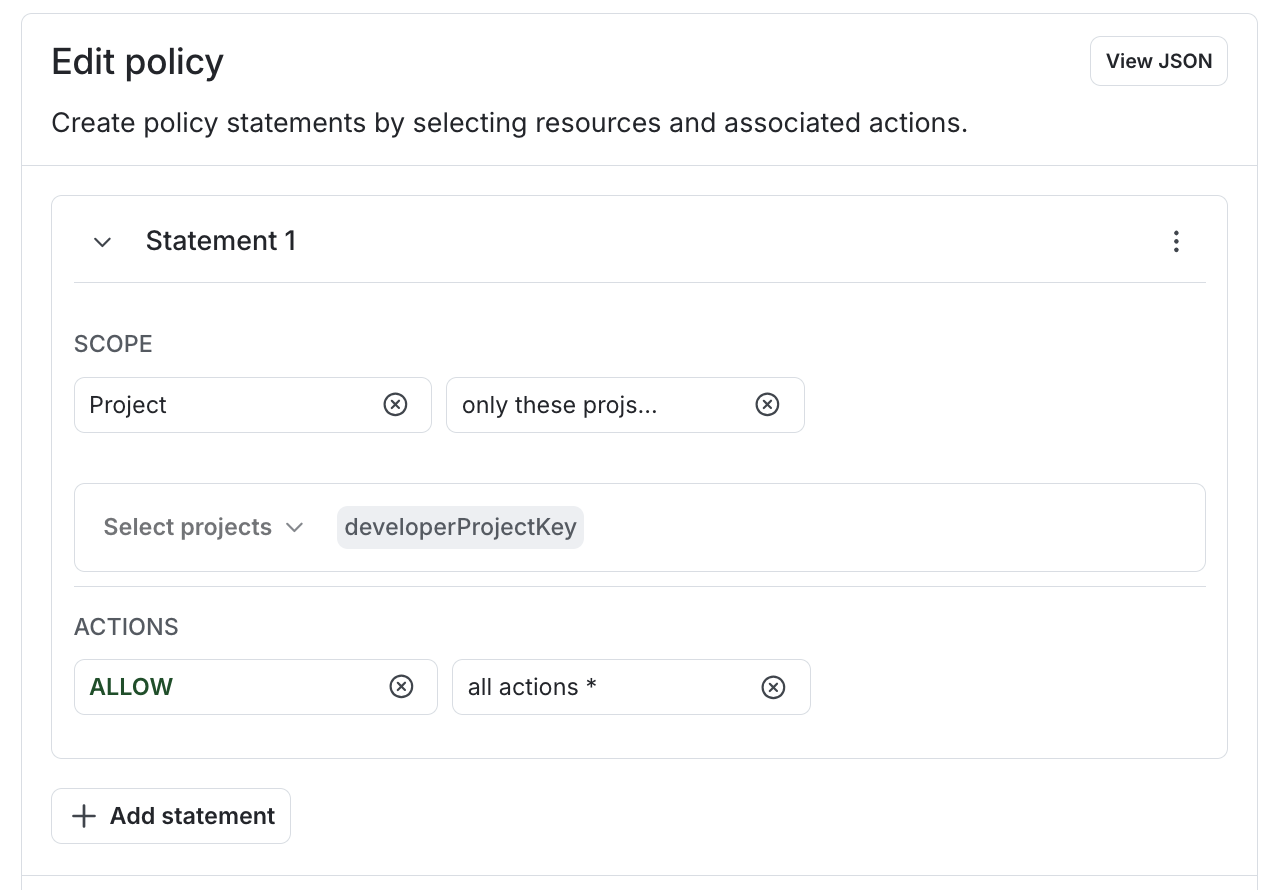
- Click Create role.
You set the value of the role attribute when you assign this role to a member or team. In this example, you would enter values for one or more project keys when you assign this role. To learn how, read Set role attribute values, below.
To learn more about creating roles, read Creating roles and policies.
Set role attribute values
You set a role attribute value, or specific resource, when you assign a role to an account member or team. In the “Assign access” dialog, enter the values for the role attribute in the Resources field:

You can enter one or more values when you set the role attribute. For example, you can set the value of the role attribute to projectA (the project key of “Project A”) when you assign the role to one member, and then set the value of the role attribute to projectB and projectC (the project keys of “Project B” and “Project C”) when you assign the role to a different member.
You can also use the REST API: Custom roles.
In the REST API, use the syntax ${roleAttribute/<attributeKey>}, for example ${roleAttribute/developerProjectKey}, in your policy statements.
To learn more, read Assigning roles to members and Assigning roles to teams.
Example: Consolidate existing roles using role attributes
Without role scope, if you have two members who require a similar set of permissions, but require access to different flags, you need to define two roles, one for each member:
Given additional flags, or additional projects, the number of roles required increases rapidly, and quickly becomes unmanageable.
You can use role scope to define just one role. Then, you can assign the same role to both members.
Here’s the previous set of roles, rewritten to use the flagKey role attribute:
When you assign this role to each member, you set the value of flagKey to the specific flag that that member should have access to.
You can use multiple role attributes in a given role. For example, if you also wanted to parameterize the project, you could use a separate role attribute for that:
In this case, LaunchDarkly prompts you to set the value of both role attributes when you assign the role to a member.
For additional examples of roles defined using role attributes, read:
- Example: Grant all actions to just one flag while showing only one project
- Example: Restrict actions within production environments
- Example: Allow access to flags, metrics, and segments in one project
Special cases for role scope
For some policy statements, you may need a combination of the advanced editor and the REST API to define a policy that uses role scope or to set role attribute values.
Use views in complex policy statements
You can define a role scope for a view when you create a role.
The policy builder supports using the viewKey role attribute in a statement with a “view” resource scope. Here’s an example policy:
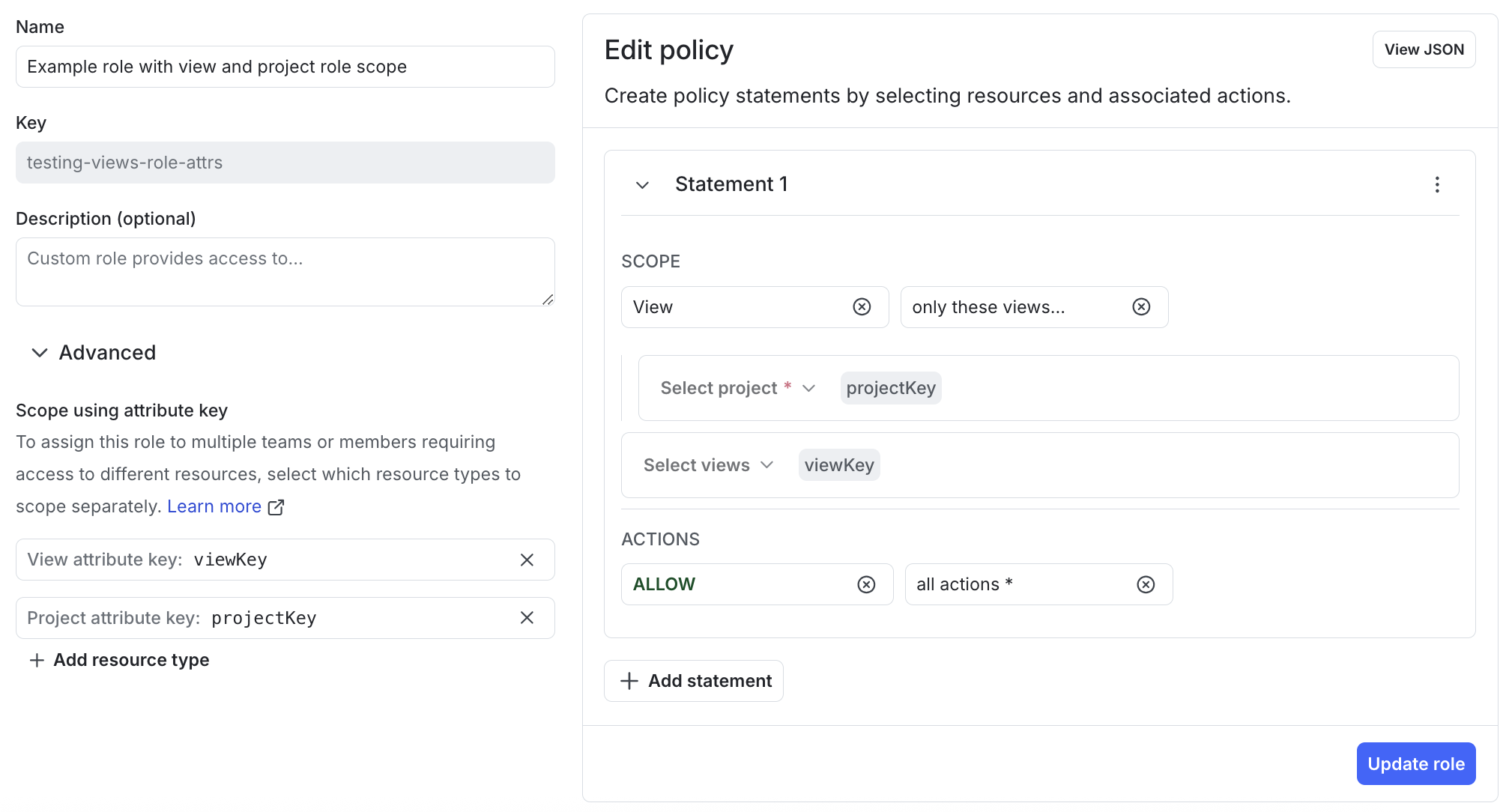
This statement allows access to all actions on the views specified by viewKey in the project specified by projectKey.
In the advanced editor, the statement looks like this:
You can also use a view role attribute in a flag scope statement. Here’s an example:
This statement allows access to all actions on flags in the project specified by projectKey, in all environments, provided the flags are linked to the view specified by viewKey.
If the viewKey role attribute is only used in a selector, LaunchDarkly may not prompt you to set its value when you assign this role to a member or team using the LaunchDarkly UI. If this happens, use the Modify an account member REST API to set the value of the role attribute.
Here’s an example request body that gives the viewKey role attribute a value of exampleView for a member:
Tags and role scope
You cannot use role attributes in tag-based policy statements.
For most role-scoping use cases, use views instead of tags. Views provide a supported way to group resources and assign access within a project. To learn more, read Onboarding to views and Use views in complex policy statements.
