Release policies
Overview
This topic explains how to use release policies to define preferred release methods for environments and standardize how your organization configures feature releases.
Release policies help organizations create consistent, measurable release practices. They set preferred release methods for specific environments and define default configurations for progressive and guarded releases. Defining these defaults at the project level promotes safer and more reliable releases.
The Release settings panel includes both release policies and release pipelines:
- Use release policies to define the default methods and configurations for new releases.
- Use release pipelines to standardize how your organization delivers releases.
Together, these tools help your organization manage rollout strategy and processes.
Use release policies to:
- Reinforce consistent release practices across your organization
- Encourage safer release methods in production
- Prevent risky or inconsistent release setups
- Improve adoption of progressive and guarded releases
Each release uses a release method to control how a new variation is served to contexts. LaunchDarkly supports the following release methods:
- Manual release: delivers a specific variation to all targeted contexts without staging. This is the default method.
- Percentage release: delivers a variation to a fixed percentage of contexts.
- Progressive release: gradually increases the percentage of contexts that receive a flag variation over time.
- Guarded release: gradually increases the number of contexts served the new flag variation while monitoring metrics for regressions.
Manual and percentage releases are not configurable through release policies
Manual and percentage releases are valid rollout strategies but are not configurable through release policies.
To learn more about progressive and guarded releases, read Releasing features with LaunchDarkly.
Best practices for creating release policies
Release policies are most effective when they reflect your organization’s goals for rollout safety and consistency. Follow these practices to improve policy adoption and clarity:
- Create a default policy to promote consistent release methods across environments.
- Use scoped policies to apply stricter controls in production or other critical environments.
- Define default rollout settings in each policy, such as rollback behavior, stages, and metric thresholds, to reduce manual setup.
- Use clear and descriptive names so developers and project members understand when each policy applies.
Combining scoped policies with default fallbacks creates a scalable and consistent approach to feature delivery.
How release policies behave
This section explains how release policies function in LaunchDarkly, including how they guide configuration decisions, display recommendations in the UI, and determine which policy applies when more than one is defined.
Purpose and behavior
Release policies define preferred release methods and default configuration settings for one or more environments in a project. They help organizations promote consistent rollout standards and safer release practices while allowing flexibility when needed.
Recommended and displayed settings
LaunchDarkly highlights the preferred release method when you configure a flag. If your project members select a release method that differs from the policy for the environment, LaunchDarkly displays a recommended label and explains how the configuration differs. Project members can continue without adopting the recommendation.
Release policies appear in the flag targeting interface as part of the release method selection process. This allows your organization to confirm configuration choices without leaving the targeting workflow.
Scope and priority
Each policy includes a scope that defines where it applies. Assign a policy to one or more environments, or create a default policy with no defined scope. The default policy applies to all environments not already covered by another policy.
Policies can target more specific subsets of flags. You can refine scope using flag tags, flag views, context kinds, or stages. For progressive and guarded releases, policies can include configuration defaults such as rollout stages, durations, metrics, metric groups, regression thresholds, and rollback behavior.
When multiple policies apply to a flag, LaunchDarkly uses the one with the highest priority. Policy order determines priority. You can reorder policies in the Release settings panel or by using the API.
To learn more, read the Release policies API documentation.
Create and manage release policies
Create and manage release policies in the Release settings panel of each project. Use this panel to define new policies, edit existing ones, and adjust their priority order.
To create a release policy:
- Click the project dropdown. The project menu appears:
- Select Project settings.
- Select Release settings. The release settings panel appears.
-
Click Create release policy.
-
Enter a name for the policy. LaunchDarkly generates a key based on the name, which you can edit.
-
Click + Add condition. Select one or more environments or other conditions where the policy applies. To create a default policy, leave the condition list empty.
-
Under “Configure the policy,” select Progressive release or Guarded release.
-
Click Add setting to add release settings to the policy.
Progressive releases use these settings:
- Context kind: Select a context kind to use as a target for the release.
- Traffic progression: Configure how to increase the percentage of contexts that receive a variation over time.
Guarded releases use the above settings, as well as:
- Metrics: Select individual metrics and metric groups to use as release guardrail metrics. LaunchDarkly automatically adds release guardrail metrics to guarded releases where the policy applies. All release guardrail metrics must use the same context kind.
- Auto-rollback: Choose whether to revert the release automatically if LaunchDarkly detects a regression in a monitored metric.
- Minimum sample size: Specify the number of context exposures that are required in order for LaunchDarkly to make a release decision.
-
Click Create policy.
LaunchDarkly adds the new policy to the list and sets its priority based on where it appears in the list. To change which policy has priority in an environment, drag the policies into the desired order. Click the three-dot overflow menu to edit or delete a policy.
Examples
These examples show how organizations use release policies to promote safer and more consistent release practices across environments.
Require guarded releases in production
An organization wants to ensure all production releases follow a standardized risk mitigation process. To support this, it creates a default release policy that defines guarded release as the preferred method for the production environment.
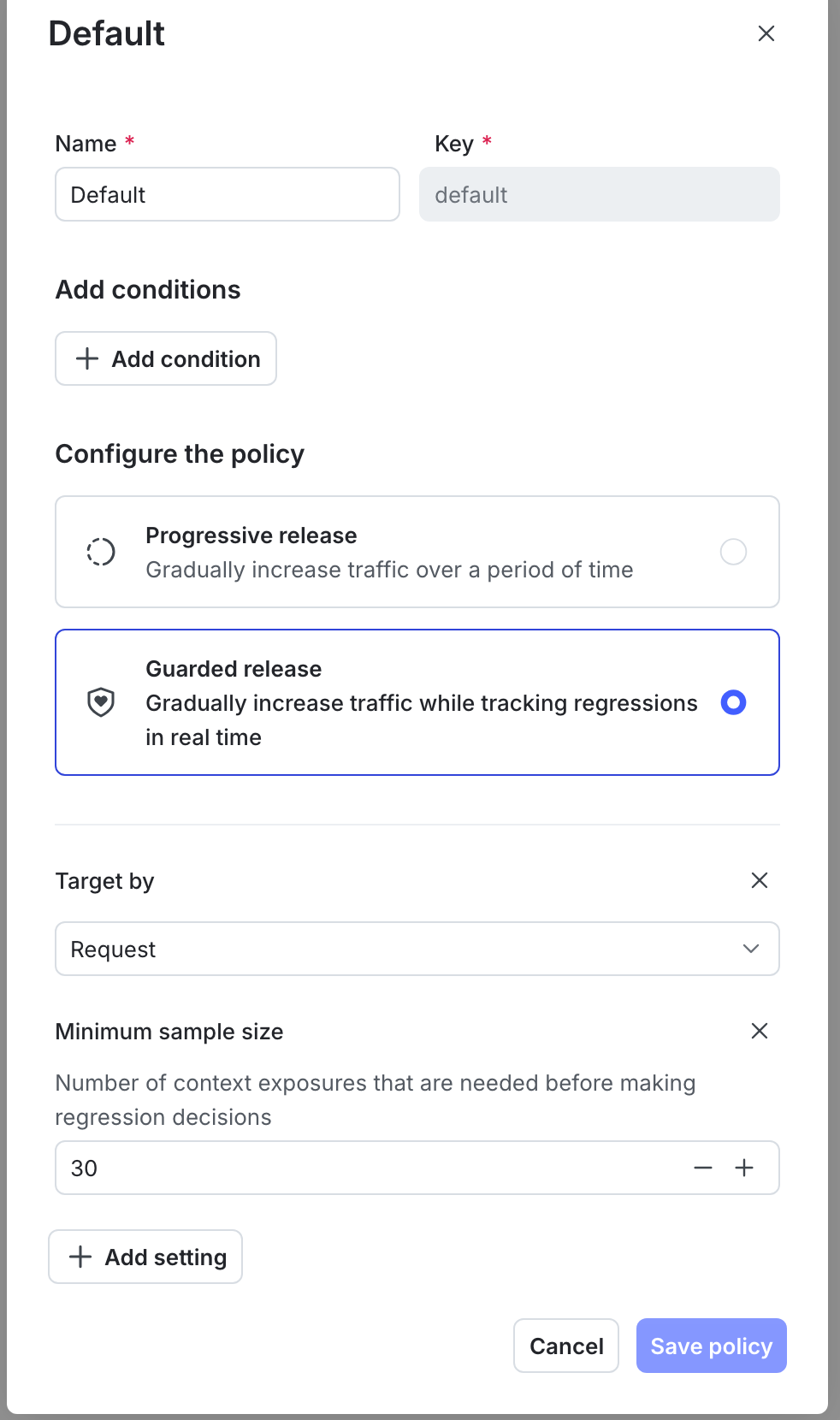
If developers select a different method, such as manual or percentage rollout, LaunchDarkly displays a recommended label to indicate that the configuration does not match the preferred policy. This helps your organization apply consistent risk checks and avoid unmonitored rollouts in critical environments.
Recommend progressive releases in staging
The organization prefers to test new features in staging using progressive releases. It creates a policy that recommends progressive releases in all staging environments.
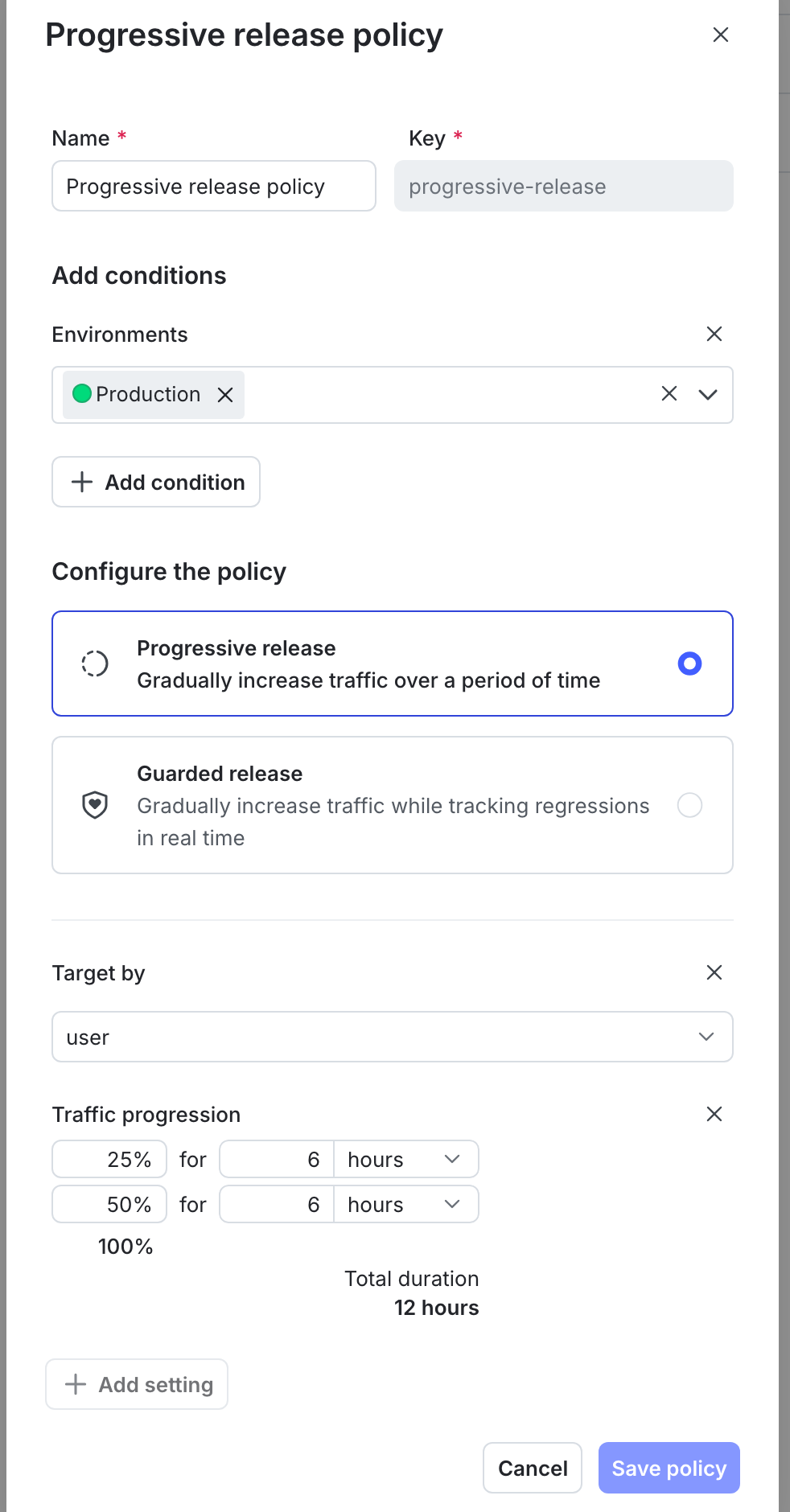
If a developer targets a flag for release in staging, LaunchDarkly highlights progressive release as the recommended method and provides configuration guidance based on the policy. This aligns your organization with its goals for staged testing and rollout readiness.