Autogenerated metrics
Overview
This topic explains the metrics LaunchDarkly automatically generates from SDK events and how you can use them to monitor the health of your applications.
Metric events
An “event” happens when someone takes an action in your app, such as clicking on a button, or when a system takes an action, such as loading a page. Your SDKs send these metric events to LaunchDarkly, where, for certain event kinds, LaunchDarkly can automatically create metrics from those events. You can use these metrics with experiments and guarded rollouts to track how your flag changes affect your customers’ behavior.
LaunchDarkly autogenerates metrics from events that are sent:
- from AI SDKs used in conjunction with AI Configs
- during document load, for browser apps, if you are using the Observability SDKs
- as part of OpenTelemetry traces using the OpenTelemetry feature for server-side SDKs
Autogenerated metrics are marked on the Metrics list with an autogenerated tag. You can view the events that autogenerated these metrics from the Metrics list by clicking View, then Events.
To learn more, read Metric events and Metric analysis.
Randomization units for autogenerated metrics
LaunchDarkly sets the randomization unit for autogenerated metrics to your account’s default context kind for experiments and guarded rollouts. For most accounts, the default context kind is user. However, you may have updated your default context kind to account, device, or some other context kind you use in experiments most often. To learn how to set the default context kind for experiments, read Mark context kinds available for experiments.
All autogenerated metrics are designed to work with a randomization unit of either user or request. Depending on your account’s default context kind for experiments, you may need to manually update the randomization unit for autogenerated metrics as needed. The recommended randomization units for each autogenerated metric are listed in the tables below. To learn how to manually update the randomization unit for a metric, read Edit metrics.
To learn more, read Randomization units.
Metrics autogenerated from AI SDK events
An AI Config is a resource that you create in LaunchDarkly and then use to customize, test, and roll out new large language models (LLMs) within your generative AI applications. As soon as you start using AI Configs in your application, you can track how your AI model generation is performing, and your AI SDKs begin sending events to LaunchDarkly.
AI SDK events are prefixed with $ld:ai and LaunchDarkly automatically generates metrics from these events.
Some events generate multiple metrics that measure different aspects of the same event. For example, the $ld:ai:feedback:user:positive event generates a metric that measures the average number of positive feedback events per user, and a metric that measures the percentage of users that generated positive feedback.
The following expandable sections explain the metrics that LaunchDarkly autogenerates from AI SDK events:
Positive AI feedback count $ld:ai:feedback:user:positive
Positive AI feedback count $ld:ai:feedback:user:positive
Metric kind: Custom conversion count
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Count
- Unit aggregation method: Sum
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Higher is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Average number of positive feedback events per context
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation causes more users to click “thumbs up”
Positive AI feedback rate $ld:ai:feedback:user:positive
Positive AI feedback rate $ld:ai:feedback:user:positive
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Higher is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Percentage of contexts that generated positive AI feedback
Example usage: Running a guarded rollout to make sure there is a positive feedback ratio throughout the rollout
Negative AI feedback count $ld:ai:feedback:user:negative
Negative AI feedback count $ld:ai:feedback:user:negative
Metric kind: Custom conversion count
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Count
- Unit aggregation method: Sum
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Average number of negative feedback events per context
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation causes more users to click “thumbs down”
Negative AI feedback rate $ld:ai:feedback:user:negative
Negative AI feedback rate $ld:ai:feedback:user:negative
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Percentage of contexts that generated negative AI feedback
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation causes more users to click “thumbs down”
Average input tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:input
Average input tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:input
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Higher is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: For example, for a chatbot, this might indicate user engagement
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation generates more input tokens, indicated better engagement
Average output tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:output
Average output tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:output
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Indicator of cost, when charged by token usage
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation results in fewer output tokens, reducing cost
Average total tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:total
Average total tokens per AI completion $ld:ai:tokens:total
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Indicator of cost, when charged by token usage
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation results in fewer total tokens, reducing cost
Average AI completion time $ld:ai:duration:total
Average AI completion time $ld:ai:duration:total
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Time required for LLM to finish a completion
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation results in faster user completion, improving engagement
AI completion success count $ld:ai:generation:success
AI completion success count $ld:ai:generation:success
Metric kind: Custom conversion count
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Count
- Unit aggregation method: Sum
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Higher is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Counter for successful LLM completion requests
Example usage: Running an experiment to find out which variation results in more user completion requests (“chattiness”), improving engagement
AI completion error count $ld:ai:generation:error
AI completion error count $ld:ai:generation:error
Metric kind: Custom conversion count
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Count
- Unit aggregation method: Sum
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Counter for erroneous LLM completion requests
Example usage: Running a guarded rollout to make sure the change doesn’t result in a higher number of errors
Average time to first token for AI requests $ld:ai:tokens:ttf
Average time to first token for AI requests $ld:ai:tokens:ttf
Metric kind: Custom Numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Time required for LLM to generate first token
Example usage: Running a guarded rollout to make sure the change doesn’t result in longer token generation times
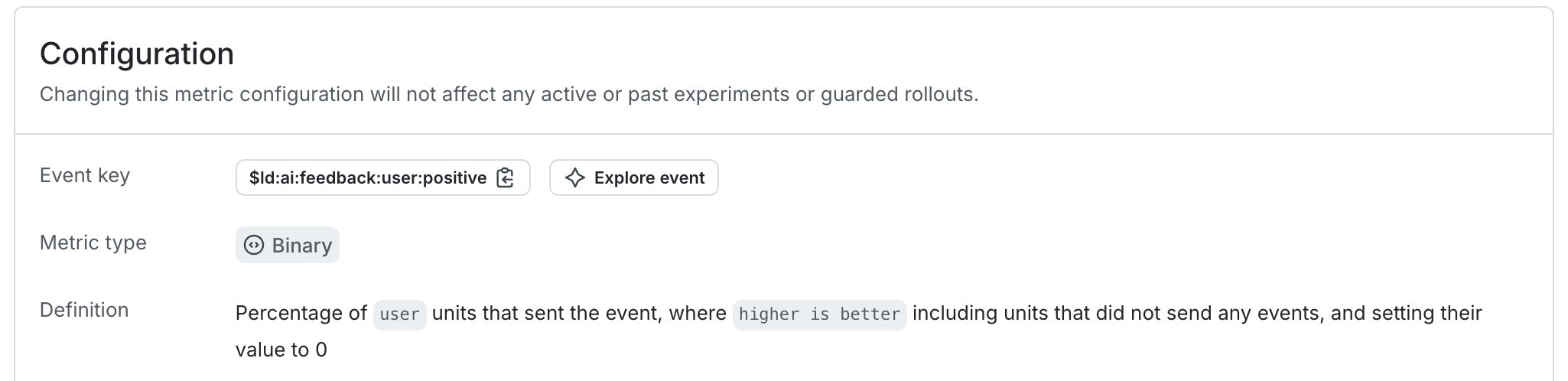
As an example, the autogenerated metric in the first expandable section above tracks the average number of positive feedback ratings per user.
Here is what the metric setup looks like in the LaunchDarkly user interface:
Metrics autogenerated from observability events
The LaunchDarkly observability SDKs provide error monitoring and metric collection for errors, web vitals, and document loading in your browser application. The functionality is in separate plugins, which you enable in the initialization options for the LaunchDarkly SDK. The observability plugins collect and send data to LaunchDarkly, where you can review metrics, events, and errors from your application.
The observability events are prefixed with $ld:telemetry and LaunchDarkly automatically generates metrics from these events.
These expandable sections explain the metrics that LaunchDarkly autogenerates from events recorded by the observability plugins for LaunchDarkly browser SDKs:
Average Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
Average Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average largest burst per context of layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifecycle of a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
P95 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile largest burst per context of layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifecycle of a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
P99 Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:cls
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile largest burst per context of layout shift scores for every unexpected layout shift that occurs during the entire lifecycle of a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Average Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
Average Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average DOM load duration in milliseconds per context
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
P95 Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile DOM load duration in milliseconds per context
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
P99 Document Load Latency per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:document_load
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile DOM load duration in milliseconds per context
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
User error rate (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:error
User error rate (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:error
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description:
Measures the percentage of contexts that encountered an error at least once. This metric is autogenerated by an initial $ld:telemetry:session:init event and populated by subsequent $ld:telemetry:error events. This means you can use the metric even if your app has not yet generated any errors.
Example usage: Running a guarded rollout to make sure the error change doesn’t result in a higher error rate
Average First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
Average First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average time in milliseconds per context between first navigation to a page and when any part of the page’s content is rendered.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
P95 First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile time in milliseconds per context between first navigation to a page and when any part of the page’s content is rendered.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
P99 First Contentful Paint (FCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile time in milliseconds per context between first navigation to a page and when any part of the page’s content is rendered.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Average First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
Average First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average time in milliseconds per context between a user’s first interaction (click, tap, or key press) and the time when the browser starts processing event handlers in response to that interaction.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
P95 First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile time, in milliseconds per context, between a user’s first interaction (click, tap, or key press) and the time when the browser starts processing event handlers in response to that interaction.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
P99 First Input Delay (FID) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:fid
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile time, in milliseconds per context, between a user’s first interaction (click, tap, or key press) and the time when the browser starts processing event handlers in response to that interaction.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Average Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
Average Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average response time in milliseconds per context of all click, tap, and keyboard interactions during the lifespan of a visit to a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
P95 Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile response time in milliseconds per context of all click, tap, and keyboard interactions during the lifespan of a visit to a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
P99 Interaction to Next Paint (INP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:inp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile response time in milliseconds per context of all click, tap, and keyboard interactions during the lifespan of a visit to a page.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Average Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
Average Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average time in milliseconds per context to render the largest image, text block, or video visible when first navigating to a page
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
P95 Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile time in milliseconds per context to render the largest image, text block, or video visible when first navigating to a page
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
P99 Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:lcp
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile time in milliseconds per context to render the largest image, text block, or video visible when first navigating to a page
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Average Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
Average Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the average time in milliseconds per context between the request for a resource and when the first byte of a response begins to arrive.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P95 Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
P95 Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 95th percentile time in milliseconds per context between the request for a resource and when the first byte of a response begins to arrive.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
P99 Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
P99 Time to First Byte (TTFB) per context (LaunchDarkly) $ld:telemetry:metric:ttfb
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events from the analysis
Description: Measures the 99th percentile time in milliseconds per context between the request for a resource and when the first byte of a response begins to arrive.
Example usage: Observing the latency of interactions an end user makes with your application
Metrics autogenerated from OpenTelemetry data
LaunchDarkly’s SDKs support instrumentation for OpenTelemetry traces. Traces provide an overview of how your application handles requests. For example, traces may show that a particular feature flag was evaluated for a particular context as part of a given HTTP request. When LaunchDarkly receives OpenTelemetry trace data, it processes and converts this data into events that LaunchDarkly metrics track over time.
There are two types of events that LaunchDarkly creates from OpenTelemetry traces: route-specific events and global events. Route-specific events are useful when you are experimenting with a change that is known to impact a small subset of your server’s HTTP routes. Global events are useful when you believe your change may impact all routes, or when you are not sure of the impact of your change.
To learn more, read OpenTelemetry for server-side SDKs.
OpenTelemetry events are prefixed with otel. LaunchDarkly automatically creates the following metrics from the events that LaunchDarkly produces from your OpenTelemetry trace data. This trace data includes the feature flag and the context for which you evaluated the flag. You can also create these metrics manually if you wish.
These expandable sections explain the metrics that LaunchDarkly autogenerates from OpenTelemetry traces:
User HTTP error rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.error
User HTTP error rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.error
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Measures the percentage of users that encountered an error inside HTTP spans at least once, as reported by OpenTelemetry. Useful when running a guarded rollout.
Per-route HTTP request errors http.error;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Per-route HTTP request errors http.error;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Examples:
http.error;method=GET;route=/api/v2/flagshttp.error;method=PATCH;route=/api/v2/flags/{id}
User HTTP 5XX response rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.5XX
User HTTP 5XX response rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.5XX
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Measures the percentage of users that encountered an HTTP 5XX response at least once, as reported by OpenTelemetry. Useful when running a guarded rollout.
Per-route HTTP 5XXs (OpenTelemetry) http.5XX;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Per-route HTTP 5XXs (OpenTelemetry) http.5XX;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Examples:
http.5XX;method=GET;route=/api/v2/flagshttp.5XX;method=PATCH;route=/api/v2/flags/{id}
User non-HTTP exception rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.exception
User non-HTTP exception rate (OpenTelemetry) otel.exception
Metric kind: Custom conversion binary
Suggested randomization unit: User
Definition:
- Measurement method: Occurrence
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Include units that did not send any events and set their value to 0
Description: Measures the percentage of users that encountered an exception outside of HTTP spans at least once, as reported by OpenTelemetry. Useful when running a guarded rollout.
Average request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
Average request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Measures the average request latency, as reported by OpenTelemetry. Useful when running a guarded rollout. For best results, use a ‘request’ randomization unit and send ‘request’ contexts.
P95 request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
P95 request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P95
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Measures the 95th percentile request latency, as reported by OpenTelemetry. For many applications, this represents the experience for most requests. You can adjust the percentile to fit your application’s needs. Useful when running a guarded rollout. For best results, use a ‘request’ randomization unit and send ‘request’ contexts.
P99 request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
P99 request latency (OpenTelemetry) otel.http.latency
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: P99
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Description: Measures the 99th percentile request latency, as reported by OpenTelemetry. For many applications, this represents the worst-case experiences. You can adjust the percentile to fit your application’s needs. Useful when running a guarded rollout. For best results, use a ‘request’ randomization unit and send ‘request’ contexts.
Per-route HTTP request latency (OpenTelemetry) http.latency;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Per-route HTTP request latency (OpenTelemetry) http.latency;method={http.request.method};route={http.route}
Metric kind: Custom numeric
Suggested randomization unit: Request
Definition:
- Measurement method: Value/size
- Unit aggregation method: Average
- Analysis method: Average
- Success criterion: Lower is better
- Units without events: Exclude units that did not send any events
Examples:
http.latency;method=GET;route=/api/v2/flagshttp.latency;method=PATCH;route=/api/v2/flags/{id}