Filtering the Contexts list
Overview
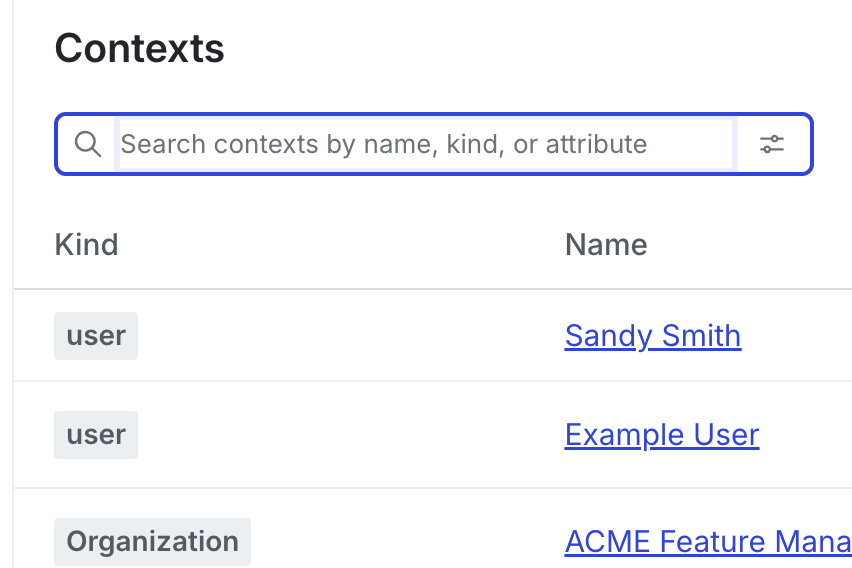
This topic explains how to filter contexts on the Contexts list. You can filter contexts on the Contexts list by context kind, name, key, or attribute.
Filter contexts
To filter contexts:
- Click the filter icon and filter the list by context kind or attribute:

- Alternatively, in the filter field, enter all or the beginning of a context kind, name, key, or attribute.
- To filter by an attribute for a specific context kind, separate the context kind and its attribute with a period (
.). For example, to search the “state” attribute of “user” contexts, useuser.state.
- Press enter. Only contexts with matching attribute values now display on the Contexts list.
You can also use the REST API: Search for contexts, Search for context instances
Advanced filter strings
In addition to filtering by context kind, name, or attribute, you can create advanced filter strings to search for specific values in specific fields.
This table contains examples of advanced filter strings and what they search for:
Elements of a filter string
A filter string contains three elements:
- Field: The field is the first part of the filter string. It is a field in the contexts that you want to filter based on.
- If you’re searching an attribute for a specific context kind, separate the context kind and its attribute with a period (
.). - Field names are always strings. If they appear within double quotes (
"), then they are encoded as if they were a JSON string. Unquoted strings must escape commas,, pipes|, parentheses(), exclamation points!, slashes\, and whitespace by prefixing the character with\.
- If you’re searching an attribute for a specific context kind, separate the context kind and its attribute with a period (
- Operator: The operator is the second part of the filter string. It describes the conditions by which the filter identifies the match value. To learn about all of the available operators, view the “Operators” table below.
- Match value: The match value is the third part of the filter string. It describes the values that the filter will identify.
- A match value must be formatted as a JSON value or an unquoted string.
- Unquoted strings must escape commas
,, pipes|, parentheses(), exclamation points!, slashes\, and whitespace by prefixing the character with\.
Operators
This table lists all of the available operators and related examples:
Save filtered contexts lists
You can create shortcuts to filtered contexts lists, and save them in the left sidenav to return to at any time. When you create a shortcut, it is only visible to you.
To create a shortcut to a filtered contexts list:
- Navigate to the Contexts list.
- Add your desired environments to the Contexts list following the instructions in Open environments.
- Add any context filters you need such as kind or attribute.
- Click the bolt icon above the Contexts list to create a shortcut:
- Add a Name for your shortcut.
- (Optional) Choose an Icon to represent your shortcut in the left sidenav.
- Click Save.
Your shortcut appears in the left sidenav.

